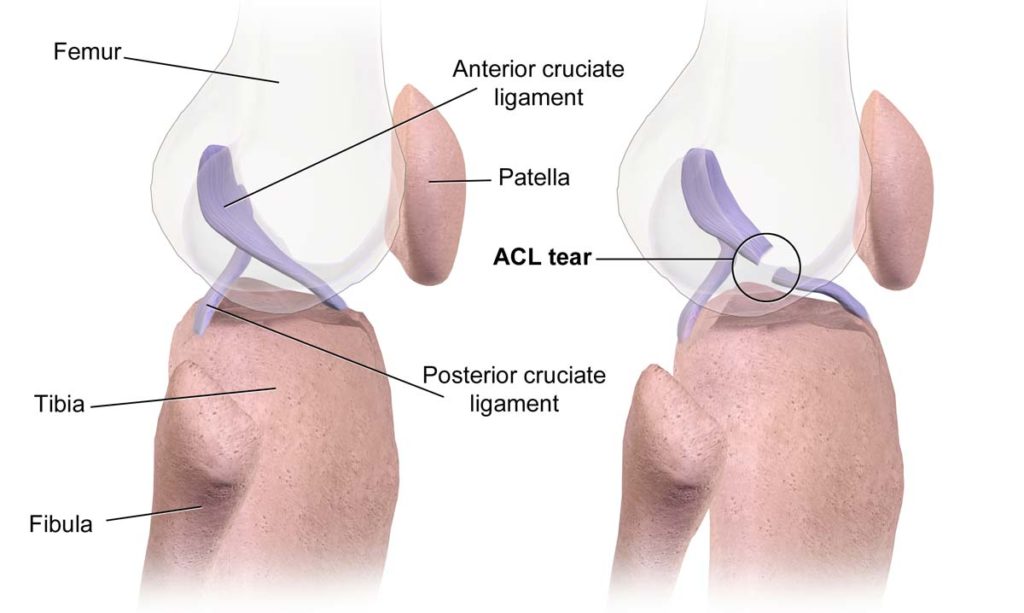
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury
Typical Symptoms
When the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is injured (torn), individuals usually experience a snapping or popping sensation in the knee followed by swelling, limited movement and instability. There might be difficulty with weight bearing on the injured knee afterwards.
What causes it?
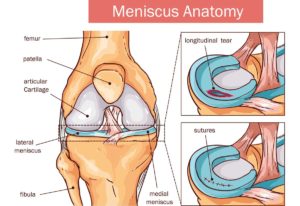
The ACL sits within the knee joint and has important role in maintaining stability. It is usually injured following a twisting movement when the foot is planted in one position and someone is changing direction suddenly or moving with force. Although it can, it does not often occur following contact.
There can also be a concurrent injury to the medial collateral ligament (MCL) or the medial meniscus (MM) and also fractures to the tibia.
How can I help myself?
It is useful to think back to the injury and how it happened. It will help understand what the mechanism might be and what might be injured. If there is considerable swelling, simple PRICE measures can help reduce this but care must be taken not to injure the skin.
If there is pain with walking or activity, offloading the knee with crutches and applying a support or compression can help it feel more stable. If pain is limiting you, analgesia can help, particularly anti-inflammatories.
When to seek help?
If your symptoms are considerable, with pain, swelling, significantly impacted function and instability, then you should be assessed as soon as possible.
What are the treatment options?
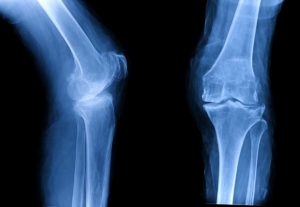
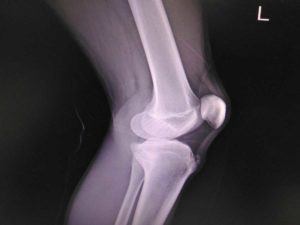
Your clinician will assess you with a thorough history and examination; they may obtain an initial X-ray of the knee to look for a bony injury such as an avulsion fracture. But in situations where an ACL/MCL injury is suspected, they may perform an ultrasound scan to look for the latter and provide a brace if necessary. If pain and swelling are significant, they may recommend crutches and commence rehabilitation with a physiotherapist to aid recovery.
To determine if the ACL has been injured, other than their clinical assessment, your clinician may request an MRI together with a surgical consult if this is confirmed; however, not all patients require surgical reconstruction of an ACL, particularly if you do not participate in pivoting sports (such as rugby, football, basketball, badminton etc).