Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)
What is it?
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive treatment in which a device is used to pass acoustic shockwaves through the skin to the affected area.
Possible mechanisms on how ESWT works have been proposed including: over‐stimulation of pain nerve fibre endings producing an analgesic effect (Melzack 1975; Rompe 1996) or disruption of the tendon tissue by the physical effects of the sound waves resulting in induction of a healing process of the tendon (Loew 1997). (Buchbinder R, Johnston RV, Roos JF. Shock wave therapy for rotator cuff disease with or without calcification. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 1. Art. No.: CD008962).
What does it involve?
An ultrasound scan or other forms of imaging are done before the procedure. This helps the clinician decide where to direct the shockwave to. Ultrasound guidance may be used to assist in positioning of the device.
Shockwaves are delivered when the machine is placed against the area that requires treatment. Ultrasound gel is needed to help the machine transmit the shocks. There are different treatment regimes and protocols depending on the condition.
What can be treated?
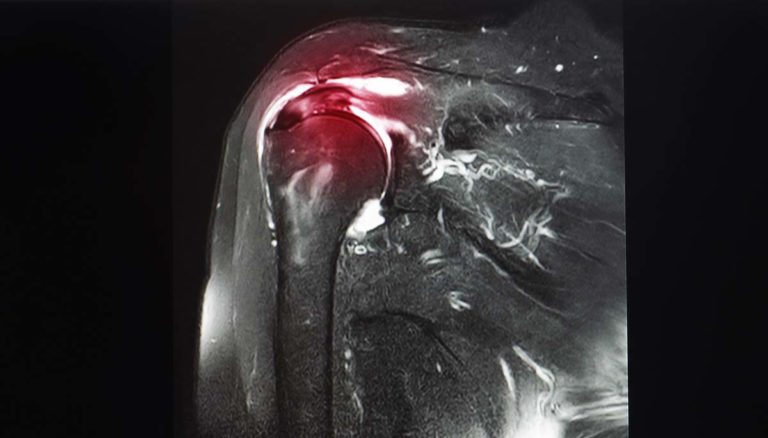
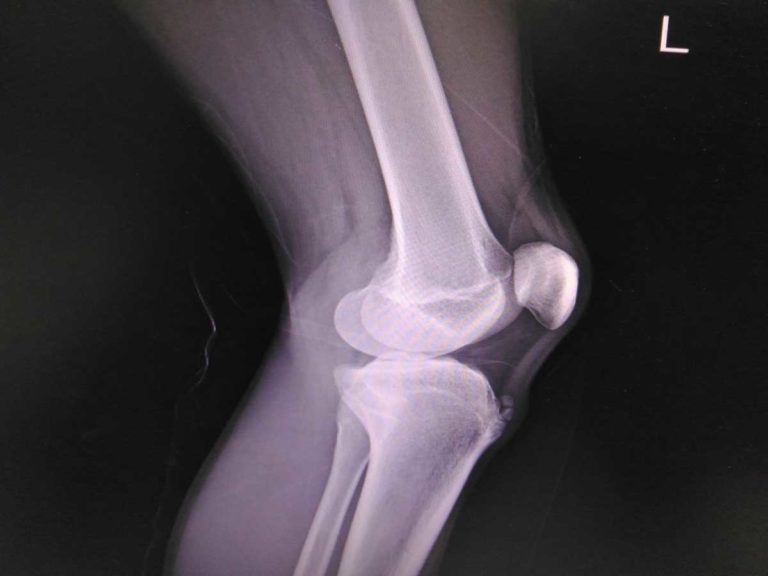
ESWT can be used to treat a variety of conditions including plantar fasciitis, achilles tendinopathy, rotator cuff tendinopathy (with or without calcification), patella tendinopathy, quadriceps tendinopathy, lateral epicondylitis of the elbow (aka tennis elbow).
What are the benefits, risks, and side effects?
Benefits
Reduction of pain and improved function.
Risks
Relatively safe procedure with no significant risks.
Side effects
Skin bruising/reddening, pain during procedure, temporary flare of pain after the procedure, recurrence of pain, damage to soft tissues.
What do I need to do afterwards?
It is important to offload the treatment site and rest from activities for a period of time. The time frame for recovery may vary on an individual basis, but most people, it it recommended to try 2-3 treatments before deciding if ESWT is beneficial. Your clinician may advise you according to your own progress and response to the treatment.
What are the common misconceptions?
ESWT needs to be combined with your other rehabilitation/treatments. By itself, it can help with pain symptoms, but when undertaken as part of a combined treatment will be more effective.