Thumb Osteoarthritis
Typical Symptoms
Osteoarthritis (OA) of the thumb joint can lead to pain, stiffness, limited movement, swelling and functional impairment of the joint. It can be at the base of the thumb, just before the wrist, or in the thumb itself.
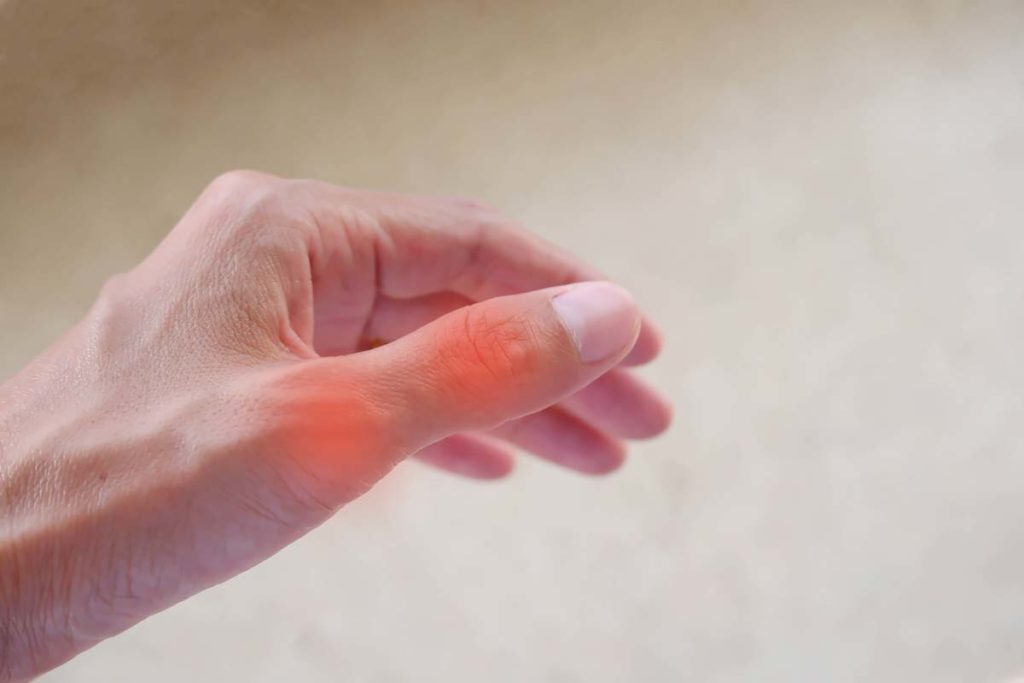
What causes it?
OA is a degenerative (wear and tear) process that is usually blamed on “over-activity”, but is more commonly due to a previous injury to the joint. However, with modern computer and smartphone usage, there is increased use of the thumb compared to previously and this can lead to the increased wear and degeneration.
How can I help myself?
In pain-limited cases, using splints, limiting load on the thumb and applying anti-inflammatory gels can help reduce symptoms.
Modifying activities or using aids to help with gripping activities or placing smartphones and computers in better positions can decrease the load on the joint.
When to seek help?
If your symptoms (pain or limited movement) are interfering with your daily, occupation or recreational activities, or there is a progression, it might be suitable to seek further attention.
What are the treatment options?
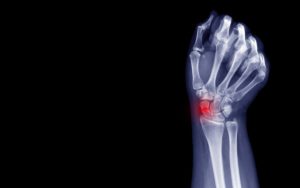
Once your clinician has assessed you thoroughly with a history and clinical examination, they may organise an X-ray of the thumb to look for bony changes or an ultrasound scan to look for joint swelling. If suitable, hand or physiotherapy can be instigated to help pain around the joint and improve strength.
In situations where pain symptoms limit these activities, an ultrasound-guided injection of cortisone or PRP injection might help reduce symptoms. If this ineffective, a surgical intervention might be appropriate with treatment tailored according to symptoms.